Fractional-order Chaos Gallery
[1]:
import brainpy as bp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
[24]:
bp.__version__
[24]:
'2.4.3'
[2]:
def plot_runner_3d(runner):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
plt.plot(runner.mon.x.flatten(),
runner.mon.y.flatten(),
runner.mon.z.flatten())
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
ax.set_zlabel('z')
plt.show()
[3]:
def plot_runner_2d(runner):
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.plot(runner.mon.x.flatten(), runner.mon.y.flatten())
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.plot(runner.mon.x.flatten(), runner.mon.z.flatten())
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('z')
plt.show()
Fractional-order Chua system
The fractional-order Chua’s system is given by [1]
[4]:
a, b, c = 10.725, 10.593, 0.268
m0, m1 = -1.1726, -0.7872
def chua_system(x, y, z, t):
f = m1 * x + 0.5 * (m0 - m1) * (abs(x + 1) - abs(x - 1))
dx = a * (y - x - f)
dy = x - y + z
dz = -b * y - c * z
return dx, dy, dz
[5]:
dt = 0.001
duration = 200
inits = [0.2, -0.1, 0.1]
integrator = bp.fde.GLShortMemory(chua_system,
alpha=[0.93, 0.99, 0.92],
num_memory=1000,
inits=inits)
runner = bp.IntegratorRunner(integrator,
monitors=list('xyz'),
inits=inits,
dt=dt)
runner.run(duration)
No GPU/TPU found, falling back to CPU. (Set TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=0 and rerun for more info.)
[6]:
plot_runner_3d(runner)
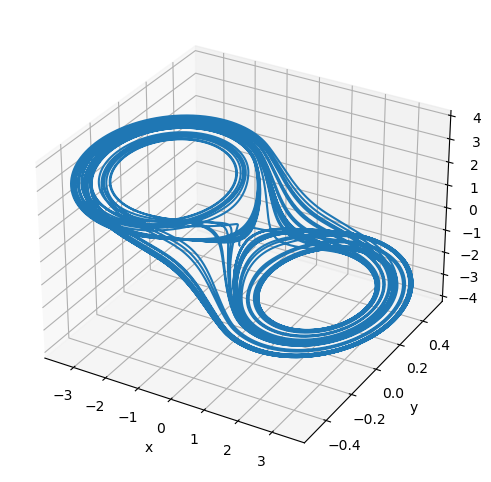
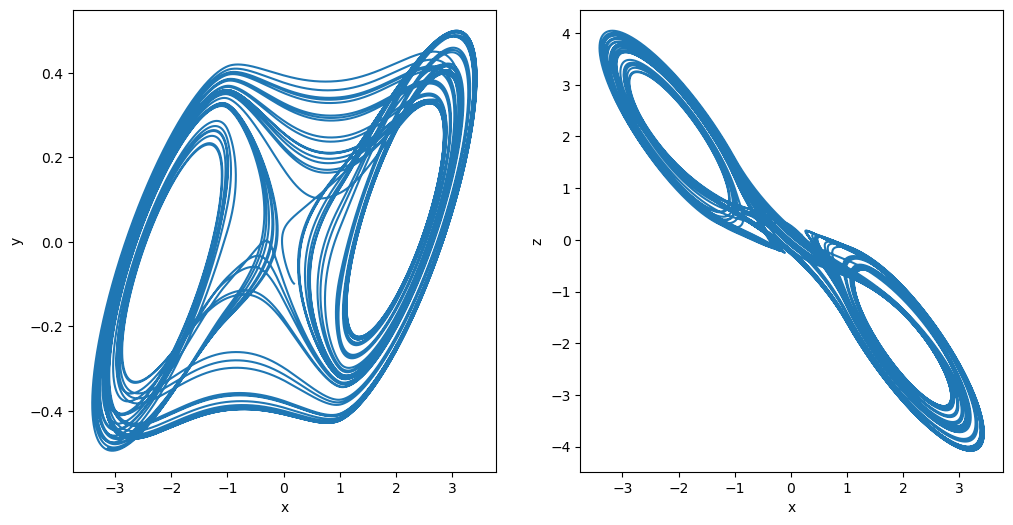
[7]:
plot_runner_2d(runner)
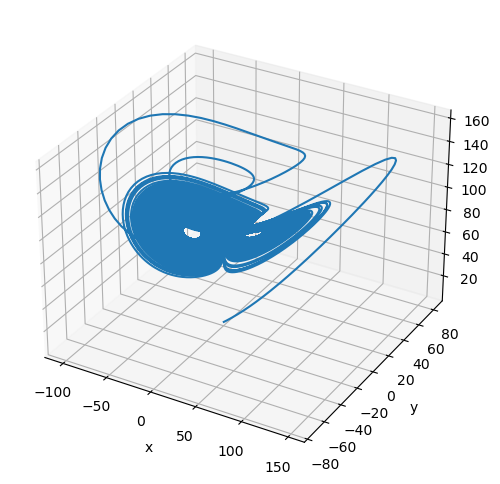
Fractional-order Qi System
The fractional-order Qi chaotic system is given by
[8]:
a, b, c = 35, 8 / 3, 80
def qi_system(x, y, z, t):
dx = -a * x + a * y + y * z
dy = c * x - y - x * z
dz = -b * z + x * y
return dx, dy, dz
[9]:
dt = 0.001
duration = 200
inits = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3]
integrator = bp.fde.GLShortMemory(qi_system,
alpha=0.98,
num_memory=1000,
inits=inits)
runner = bp.IntegratorRunner(integrator,
monitors=list('xyz'),
inits=inits,
dt=dt)
runner.run(duration)
[10]:
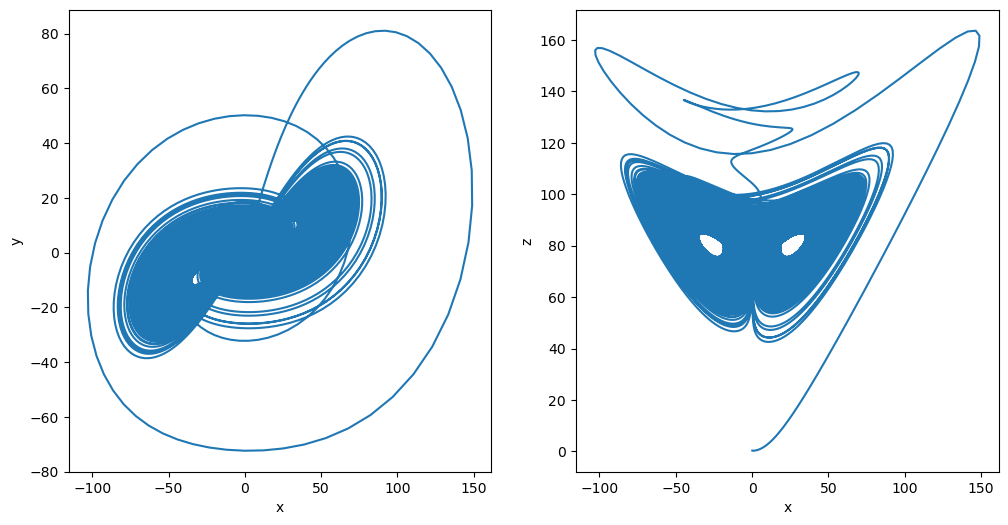
plot_runner_3d(runner)
[11]:
plot_runner_2d(runner)
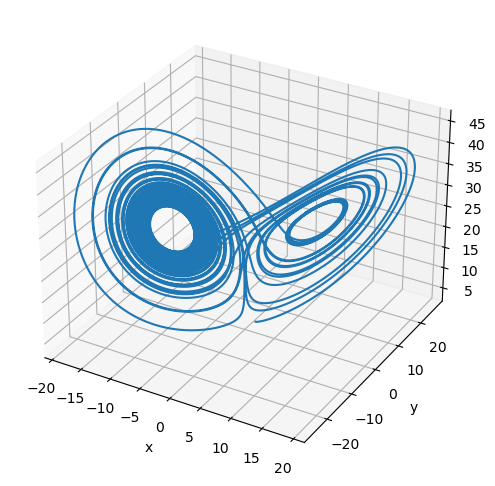
Fractional-order Lorenz System
The fractional-order Lorenz system is given by [3]
[12]:
a, b, c = 10, 28, 8 / 3
def lorenz_system(x, y, z, t):
dx = a * (y - x)
dy = x * (b - z) - y
dz = x * y - c * z
return dx, dy, dz
[13]:
dt = 0.001
duration = 50
inits = [1, 2, 3]
integrator = bp.fde.GLShortMemory(lorenz_system,
alpha=0.99, # fractional order
num_memory=1000,
inits=inits)
runner = bp.IntegratorRunner(integrator,
monitors=list('xyz'),
inits=inits,
dt=dt)
runner.run(duration)
[14]:
plot_runner_3d(runner)
[15]:
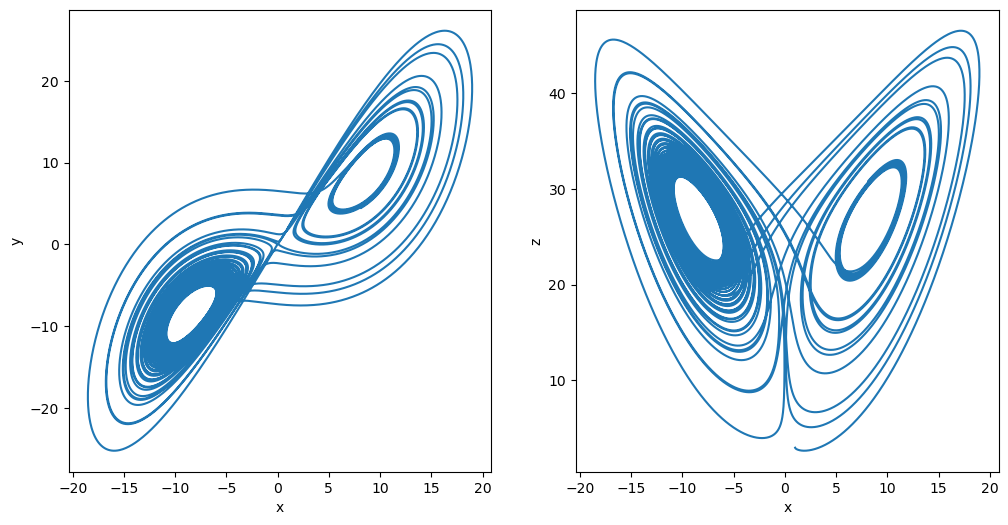
plot_runner_2d(runner)
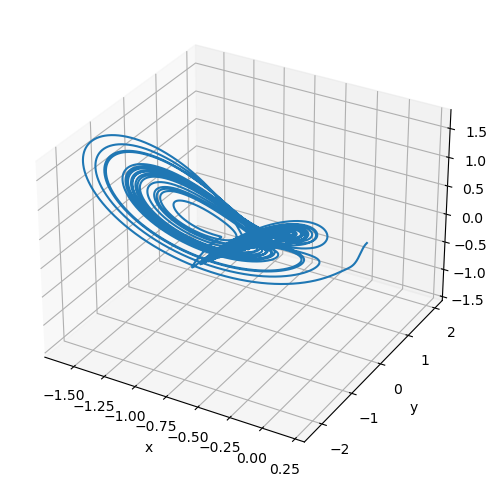
Fractional-order Liu System
The fractional order system is given by [4]
[16]:
a, b, c, e, n, m = 1, 2.5, 5, 1, 4, 4
def liu_system(x, y, z, t):
dx = -a * x - e * y ** 2
dy = b * y - n * x * z
dz = -c * z + m * x * y
return dx, dy, dz
[17]:
dt = 0.001
duration = 100
inits = [0.2, 0, 0.5]
integrator = bp.fde.GLShortMemory(liu_system,
alpha=0.95, # fractional order
num_memory=1000,
inits=inits)
runner = bp.IntegratorRunner(integrator,
monitors=list('xyz'),
inits=inits,
dt=dt)
runner.run(duration)
[18]:
plot_runner_3d(runner)
[19]:
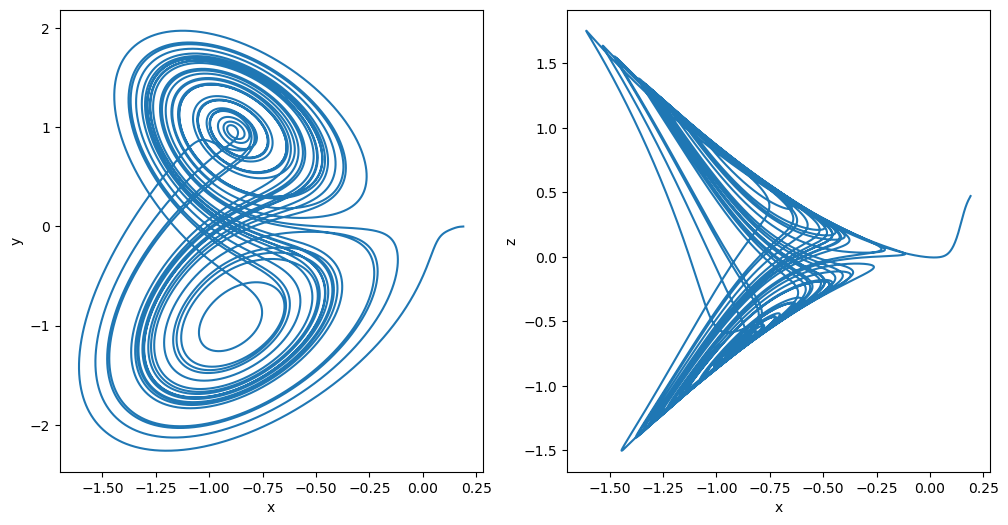
plot_runner_2d(runner)
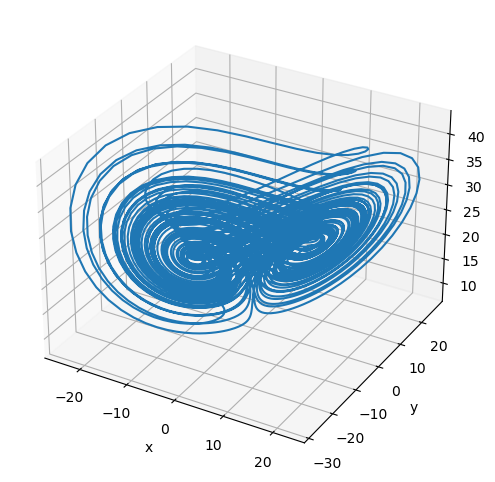
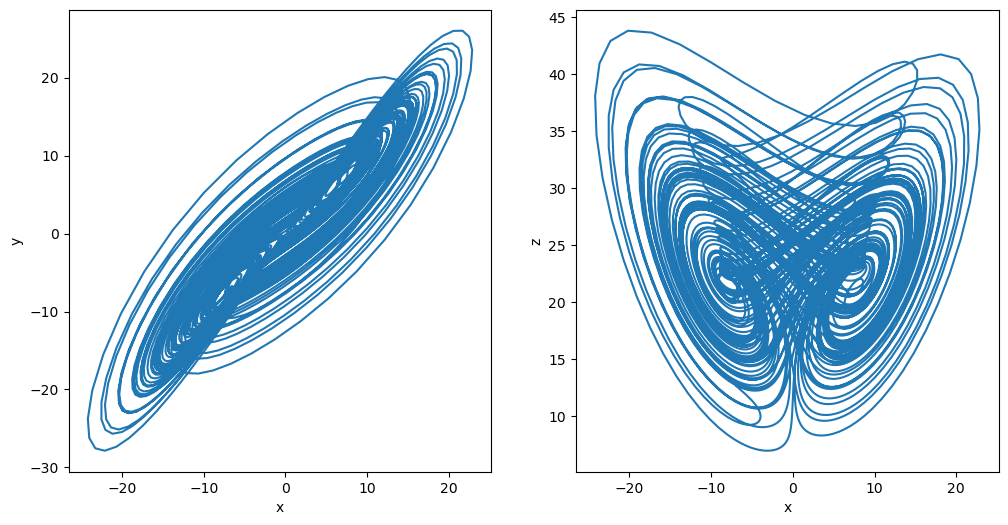
Fractional-order Chen System
The system is given by [5]
[20]:
a, b, c, d = 35, 3, 28, -7
def chen_system(x, y, z, t):
dx = a * (y - x)
dy = d * x - x * z + c * y
dz = x * y - b * z
return dx, dy, dz
[21]:
dt = 0.005
duration = 50
inits = [-9, -5, 14]
integrator = bp.fde.GLShortMemory(chen_system,
alpha=0.9, # fractional order
num_memory=1000,
inits=inits)
runner = bp.IntegratorRunner(integrator,
monitors=list('xyz'),
inits=inits,
dt=dt)
runner.run(duration)
[22]:
plot_runner_3d(runner)
[23]:
plot_runner_2d(runner)
References
[1] Petráš, Ivo. “A note on the fractional-order Chua’s system.” Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 38.1 (2008): 140-147.
[2] Wu, Xiangjun, and Yang Yang. “Chaos in the fractional-order Qi system and its synchronization using active control.” 2010 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Cognitive Informatics. IEEE, 2010.
[3] Wu, Xiang-Jun, and Shi-Lei Shen. “Chaos in the fractional-order Lorenz system.” International Journal of Computer Mathematics 86.7 (2009): 1274-1282.
[4] Daftardar-Gejji, Varsha, and Sachin Bhalekar. “Chaos in fractional ordered Liu system.” Computers & mathematics with applications 59.3 (2010): 1117-1127.
[5] Lu, Jun Guo, and Guanrong Chen. “A note on the fractional-order Chen system.” Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 27.3 (2006): 685-688.
